Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we perceive and interact with digital transactions. It is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that allows for secure, transparent, and immutable recording of transactions. This article introduces a real-world blockchain case study that showcases the potential of this innovative technology.

IBM Food Trust is a blockchain-based platform designed to enhance the transparency and traceability of the food supply chain. It allows food producers, suppliers, and retailers to record and share information about the origin, processing, and distribution of food products. Let's delve into how this platform works and its impact on the food industry.
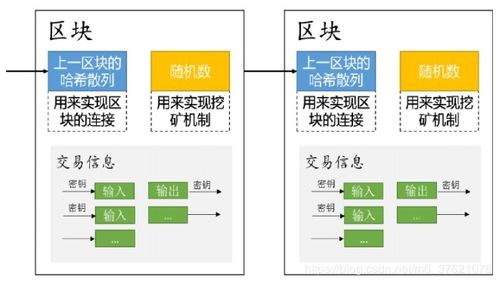
IBM Food Trust utilizes the Hyperledger Fabric blockchain platform to create a decentralized network where participants can securely share data. The platform operates on a permissioned blockchain, meaning that only authorized parties can access and contribute to the network.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how IBM Food Trust functions:
Food producers and suppliers record information about their products, such as origin, ingredients, and processing methods, onto the blockchain.
This information is then validated and stored in a new block, which is added to the chain.
Each block contains a unique cryptographic hash that links it to the previous block, ensuring the integrity and immutability of the data.
Authorized participants can access the blockchain to verify the authenticity and history of any food product.

IBM Food Trust has had a significant impact on the food industry by addressing several challenges:
Food Safety: By providing a transparent and traceable supply chain, the platform helps to identify the source of foodborne illnesses more quickly, thereby reducing the risk of outbreaks.
Consumer Trust: Consumers can access information about the products they purchase, such as where they were grown, how they were processed, and whether they contain any allergens.
Efficiency: The platform streamlines the supply chain process, reducing the time and costs associated with tracking and verifying food products.
Regulatory Compliance: Food companies can use IBM Food Trust to demonstrate compliance with various regulations, such as the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) in the United States.

While IBM Food Trust has demonstrated the potential of blockchain in the food industry, there are still challenges to be addressed:
Scalability: As the number of participants and transactions increases, the platform must ensure that it can handle the growing volume of data without compromising performance.
Interoperability: To maximize the benefits of blockchain, it is essential to develop standards and protocols that enable different platforms to communicate and share data seamlessly.
Security: While blockchain is inherently secure, it is crucial to continuously monitor and update the platform to protect against potential vulnerabilities.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain in the food industry looks promising. As more companies adopt blockchain technology, we can expect to see increased transparency, efficiency, and trust in the food supply chain.

IBM Food Trust is a compelling example of how blockchain technology can be applied to real-world problems. By enhancing the transparency and traceability of the food supply chain, the platform has the potential to improve food safety, consumer trust, and regulatory compliance. As blockchain continues to evolve, we can expect to see more innovative applications in various industries, including food, healthcare, and finance.